在初学Pytorch 创建模型的时候,总会出现不知道要把layer放在 __init()__ 中还是 forwad() 中,也不知道到底该使用nn.Conv2d还是F.conv2d。为此带来了不必要的烦恼。
我为了搞清用法查看了官方doc并在pytorch论坛上做了询问,此为讨论的链接,整理结果如下:
torch.nn
torch.nn这个模块下面存的主要是Module类。以torch.nn.Conv2d为例, 也就是说torch.nn.Conv2d这种”函数”其实是个 Module类,在实例化类后会初始化2d卷积所需要的参数。这些参数会在你做forward()和backward()之后根据loss进行更新,所以通常存放在定义模型的 __init__() 中,如:
class MyModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MyModel,self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3,6,3,1,1)
self.act = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self,x):
x=self.act(self.conv1(x))
return x
那在定义模型时,可不可以把nn.Conv2d写在forward处?
不可以
如果写成类似这样会有什么影响呢?
class MyModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MyModel, self).__init__()
self.act = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x):
# 把卷积函数写在forward中
x= nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 3, 1, 1)(x)
x = self.act(x)
return x
把nn.Conv2d写在forward()中就相当于模型每次跑forward()的时候,都重新实例化了nn.Conv2d和nn.Conv2d的参数,导致模型学不到参数。
torch.nn.functional
torch.nn.functional.x 为函数,与torch.nn不同, torch.nn.x中包含了初始化需要的参数等 attributes 而torch.nn.functional.x则需要把相应的weights 作为输入参数传递,才能完成运算, 所以用torch.nn.functional创建模型时需要创建并初始化相应参数。
例如:
import torch.nn.functional as F
class MyModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MyModel, self).__init__()
self.act = nn.ReLU()
self.weighs = nn.Parameter(torch.rand(x,x,x,x))
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.rand(x))
def forward(self, x):
# 把卷积函数写在forward中,把w和b传入函数
x= F.conv2d(x,self.weighs,self.bias)
x = self.act(x)
return x
PyTorch官方推荐用法
- 具有学习参数的(例如,
conv2d,linear,batch_norm)采用nn.Xxx方式; - 没有学习参数的(例如,
maxpool,loss func,activation func)等根据个人选择使用nn.functional.xxx或者nn.Xxx方式。
但关于dropout,个人强烈推荐使用nn.Xxx方式,因为一般情况下只有训练阶段才进行dropout,在eval阶段都不会进行dropout。使用nn.Xxx方式定义dropout,在调用model.eval()之后,model中所有的dropout layer都关闭,但以nn.function.dropout方式定义dropout,在调用model.eval()之后并不能关闭dropout。
class Model1(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model1, self).__init__()
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.5)
def forward(self, x):
return self.dropout(x)
class Model2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model2, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x):
return F.dropout(x)
m1 = Model1()
m2 = Model2()
inputs = torch.rand(10)
print(m1(inputs))
print(m2(inputs))
print(20 * '-' + "eval model:" + 20 * '-' + '\r\n')
m1.eval()
m2.eval()
print(m1(inputs))
print(m2(inputs))
输出:
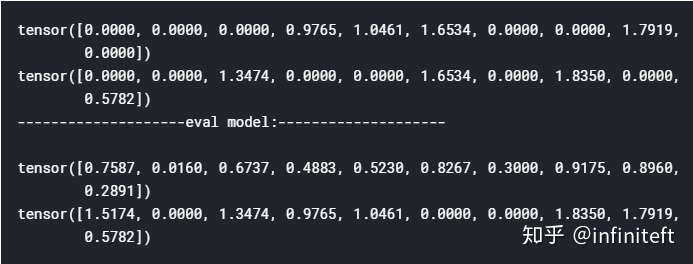
从上面输出可以看出m2调用了eval之后,dropout照样还在正常工作。当然如果你有强烈愿望坚持使用nn.functional.dropout,也可以采用下面方式来补救。
class Model3(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model3, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x):
return F.dropout(x, training=self.training)
总结
查看两者的doc即可看出区别:
torch.nn.functional.conv2d(input, weight, bias=None, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1) → Tensor
CLASS
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True, padding_mode=‘zeros’)
即一个侧重数据结构,一个侧重算法运算。 其实两个都是完成了同样的功能,只是实现方式有些不同而已:
| torch.nn.X | torch.nn.functional.X |
|---|---|
| 是类 | 是函数 |
| 结构中包含所需要初始化的参数 | 需要在函数外定义并初始化相应参数,并作为参数传入 |
一般情况下放在__init__ 中实例化,并在forward()中完成操作 |
一般在__init__ 中初始化相应参数,在forward()中传入 |
| 运行效率也是近乎相同 | 运行效率也是近乎相同 |
所以模型要么写成这样
class MyModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MyModel, self).__init__()
# which has its own hidden parameters
self.conv_like = nn.convlike()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv_like(x)
要么写成这样:
class MyModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MyModel, self).__init__()
# which will be used in nn.functional.funs
self.func_params = params
def forward(self, x):
x = nn.functional.funs(x,self.func_params)



