一、介绍
argparse是python用于解析命令行参数和选项的标准模块,用于代替已经过时的optparse模块。argparse模块的作用是用于解析命令行参数。
我们很多时候,需要用到解析命令行参数的程序。
二、使用步骤⭐
我们常常可以把argparse的使用简化成下面四个步骤
import argparseparser = argparse.ArgumentParser()parser.add_argument()parser.parse_args()
上面四个步骤解释如下:首先导入该模块;然后创建一个解析对象;然后向该对象中添加你要关注的命令行参数和选项,每一个add_argument方法对应一个你要关注的参数或选项;最后调用parse_args()方法进行解析;解析成功之后即可使用。
三、例子讲解
下面我们通过一个例子来进行讲解说明
我们可以看到上面的第二个步骤,parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
它的作用就是:当调用parser.print_help()或者运行程序时由于参数不正确(此时python解释器其实也是调用了print_help()方法)时,会打印这些描述信息,一般只需要传递description参数。
下面会有例子输出,首先给出代码:
#-*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import argparse #步骤一
def parse_args():
"""
:return:进行参数的解析
"""
description = "you should add those parameter" # 步骤二
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=description) # 这些参数都有默认值,当调用parser.print_help()或者运行程序时由于参数不正确(此时python解释器其实也是调用了pring_help()方法)时,
# 会打印这些描述信息,一般只需要传递description参数,如上。
help = "The path of address"
parser.add_argument('--addresses',help = help) # 步骤三,后面的help是我的描述
args = parser.parse_args() # 步骤四
return args
if __name__ == '__main__':
args = parse_args()
print(args.addresses) #直接这么获取即可。
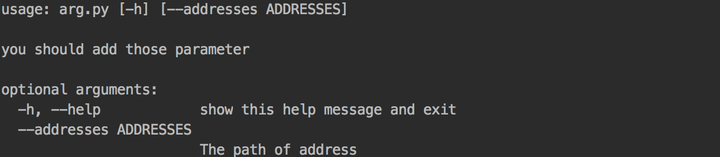
上面四个步骤已经分别对应上了,当我们在命令行敲入:
python arg.py -h
输出提示为:
四、如何获得命令参数值
我们可以直接通过args.addresses获得它的参数值。
当我们敲入python arg.py --addresses this-is-parameter-of-addresses 命令时
会输出this-is-parameter-of-addresses
到这里就总结了argparse模块常见的一些常见的用法。
五、add_argument()
用argparse模块让python脚本接收参数时,对于True/False类型的参数,向add_argument()方法中加入参数action=‘store_true’/‘store_false’。
顾名思义,store_true就代表着一旦有这个参数,做出动作“将其值标为True”,也就是没有时,默认状态下其值为False。反之亦然,store_false也就是默认为True,一旦命令中有此参数,其值则变为False。
代码如下:
ce#-*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import argparse #步骤一
def parse_args():
"""
:return:进行参数的解析
"""
description = "you should add those parameter" # 步骤二
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=description) # 这些参数都有默认值,当调用parser.print_help()或者运行程序时由于参数不正确(此时python解释器其实也是调用了pring_help()方法)时,
# 会打印这些描述信息,一般只需要传递description参数,如上。
help = "The path of address"
parser.add_argument('--addresses',default=True,action='store_false',help = help) # 步骤三,后面的help是我的描述
args = parser.parse_args() # 步骤四
return args
if __name__ == '__main__':
args = parse_args()
print(args.addresses) #直接这么获取即可。
测试结果:

Action: Arguments can trigger different actions, specified by the action argument to
add_argument(). There are six built-in actions that can be triggered when an argument is encountered:
store: Save the value, after optionally converting it to a different type. This is the default action taken if none is specified explicitly.store_true/store_false: Save the appropriate boolean value.store_const: Save a value defined as part of the argument specification, rather than a value that comes from the arguments being parsed. This is typically used to implement command line flags that aren’t booleans.append: Save the value to a list. Multiple values are saved if the argument is repeated.append_const: Save a value defined in the argument specification to a list.version: Prints version details about the program and then exits.



